
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 72.3% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Access Restricted for EU Residents.
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards. As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website. Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Monday Oct 27 2025 06:38

8 min

What is crude oil trading: Crude oil remains one of the most important commodities globally, influencing economies, industries, and markets.
Trading crude oil offers a way to participate in this vital sector, but understanding the fundamentals and different investment options is essential before starting. This guide explains what crude oil is, the basics of trading it, common investment methods, and how to begin crude oil investing using markets.com.
Crude oil is a naturally occurring substance, a fossil fuel found beneath the earth’s surface, formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms. It serves as a primary energy source and raw material for various products including gasoline, diesel, plastics, and chemicals.
The value of crude oil is influenced by supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical factors, production decisions by key oil-producing countries, and global economic conditions. Its price fluctuations can have widespread impacts across multiple sectors.
Crude oil trading involves buying and selling contracts or assets tied to the price of crude oil. Traders and investors aim to benefit from price movements, whether prices rise or fall. This can be done through various financial instruments that offer exposure to crude oil without necessarily handling the physical commodity.
Trading crude oil requires awareness of market drivers such as inventory reports, geopolitical events, production levels, and economic indicators. It is also important to choose the right vehicle for trading based on individual goals, risk tolerance, and market knowledge.
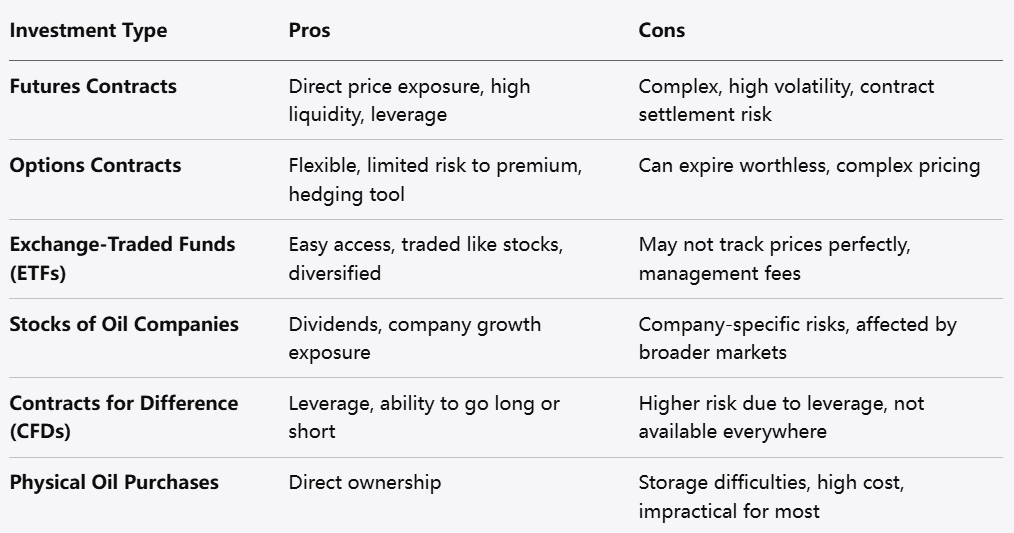
There are several ways to invest in crude oil, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Futures Contracts
Pros:
Direct exposure to crude oil price movements
High liquidity and standardized contracts
Ability to use leverage to control larger positions
Cons:
Requires understanding of contract specifications
Exposure to high volatility and potential for large losses
Obligations to settle contracts can be complex
Options Contracts
Pros:
Flexibility to buy or sell crude oil at predetermined prices
Limited risk to the premium paid for the option
Can be used for hedging or speculative purposes
Cons:
Options can expire worthless if market moves unfavorably
Pricing can be complex due to time decay and volatility factors
Requires knowledge of options strategies
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Pros:
Easy access to crude oil exposure without owning physical oil
Traded like stocks on public exchanges
Diversification through baskets of oil-related assets
Cons:
May not perfectly track crude oil prices due to fund structure
Management fees can reduce returns over time
Subject to market risks affecting ETF shares

Stocks of Oil Companies
Pros:
Exposure to oil sector through established companies
Potential for dividends and capital appreciation
Benefit from both oil prices and company performance
Cons:
Subject to company-specific risks such as management and operations
Stock prices influenced by broader market trends beyond oil prices
Dividend payments are not guaranteed
Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
Pros:
Ability to trade crude oil price movements without owning the asset
Access to leverage to enhance exposure
Opportunity to go long or short on oil prices
Cons:
Leverage increases risk of losses beyond initial margin
Overnight financing fees may apply for holding positions
Not available in all jurisdictions due to regulations
Physical Oil Purchases
Pros:
Direct ownership of crude oil or related products
Potential for use in industrial or commercial applications
Cons:
Storage and transportation challenges
High capital requirements and logistical complexities
Not practical for most individual traders

Markets.com offers a user-friendly platform enabling access to crude oil trading through CFDs and other instruments. Here is how to start:
Create an Account: Register on markets.com by providing necessary details and verifying your identity.
Fund Your Account: Deposit funds using your preferred payment method to enable trading activities.
Research Crude Oil Markets: Use available tools and resources on the platform to understand current market conditions.
Choose Your Instrument: Select crude oil CFDs or related products available for trading on markets.com.
Place Your Trade: Decide on trade size, direction (buy or sell), and place the order according to your strategy. Monitor and manage your position using the platform’s features.

Trading crude oil effectively involves strategies tailored to its unique market characteristics:
Trend Following: Identifying and trading in the direction of prevailing market trends.
Range Trading: Capitalizing on price movements within established support and resistance levels.
News-Based Trading: Reacting quickly to reports on inventory, geopolitical developments, and economic data.
Hedging: Using crude oil positions to offset risks in other parts of a portfolio.
Risk Management: Employing stop-loss orders and position sizing to control exposure.
Adapting strategies as market conditions evolve is essential for managing risks and potential outcomes.
Crude oil trading offers diverse ways to engage with one of the world’s most critical commodities. From futures and options to ETFs and CFDs, each investment vehicle presents distinct characteristics suitable for different participants.
Markets.com provides an accessible platform to begin crude oil investing, offering tools and instruments designed for various trading preferences. By understanding the basics of crude oil, the available investment options, and employing thoughtful trading strategies, individuals can navigate this dynamic market with greater confidence.
Starting with a clear plan and proper risk controls will help in managing the complexities of crude oil trading, making it a valuable addition to a diversified financial approach.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.