
Day trading basics: Day trading is an approach to the financial markets where positions are opened and closed within the same trading day.
This style of trading requires a unique mindset, discipline, and a clear strategy to navigate the fast-paced environment. While there is no single “best” method that guarantees results, there are several widely accepted principles and approaches that can guide traders in crafting a method suited to their individual style and goals. This article explores foundational concepts and practical methods for day trading.
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments—such as stocks, currencies, or futures—within a single trading session. The goal is to capitalize on short-term price movements, often leveraging market volatility to enter and exit positions quickly.
Unlike longer-term trading, day trading does not involve holding positions overnight, which helps avoid exposure to after-hours risks such as news events or market gaps. This approach demands constant attention during market hours and a readiness to act swiftly.
While strategies can vary, the best day trading methods share certain essential components:
1. Clear Entry and Exit Criteria
A successful approach begins with clearly defined rules for entering and exiting trades. This involves identifying setups where the market shows potential for a quick move in a particular direction.
Entry points are usually based on patterns, price behavior, or signals that suggest momentum. Exit points should be planned to lock in gains or limit losses, often using predetermined levels rather than emotional decision-making.
2. Risk Management
Managing risk is crucial in day trading. Since the market can move rapidly, protecting capital is a top priority. This means setting strict limits on how much of one’s capital is exposed per trade and using tools to automatically close losing positions before losses accumulate.
Proper risk management helps maintain consistency and longevity in trading, reducing the chance that a few bad trades can wipe out gains.
3. Discipline and Emotional Control
The ability to stick to a plan and avoid impulsive decisions is vital. Day trading can be stressful, with rapid price movements triggering emotional reactions. Discipline ensures adherence to strategies, avoiding chasing trades or holding losing positions hoping for reversals.
Developing emotional control is a process that comes with experience but is foundational to maintaining a steady approach.
4. Adaptability
Markets evolve throughout the day and from one session to the next. Conditions that work well in one environment may falter in another. A good day trading method includes flexibility to adjust tactics based on market volatility, volume, and broader economic factors.
Being adaptable also means recognizing when to step back from trading during uncertain or unfavorable conditions.
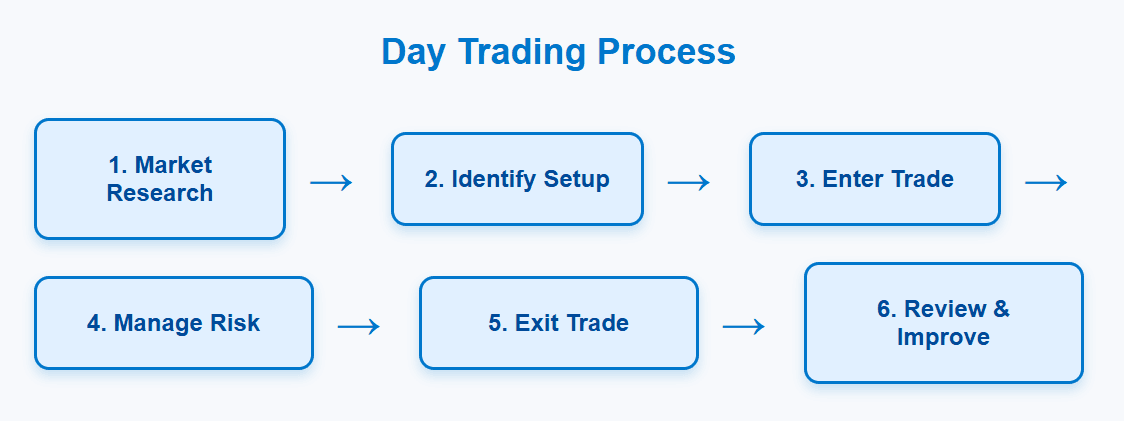
Several methods have gained prominence among day traders due to their structure and clarity. Below are some of the most commonly used approaches:
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading focuses on stocks or instruments showing strong directional movement accompanied by high volume. Traders look for accelerating price moves and aim to ride the wave until momentum wanes.
This method relies heavily on speed and timing, capitalizing on bursts of interest triggered by news or market sentiment. Momentum traders closely watch for entry signals early in a move and exit before momentum fades.
Reversal Trading
Reversal trading aims to identify price points where a current trend may lose steam and reverse direction. Traders look for signs of exhaustion or overextension in price moves to anticipate a turnaround.
This approach demands careful timing and confirmation, as premature entries can lead to losses if the trend continues.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading centers on entering trades when price moves beyond established support or resistance levels. Breakouts can signal the start of new trends or accelerated moves, providing opportunities for quick gains.
Traders watch for volume increases and other confirmations to validate breakout moves and avoid false signals.
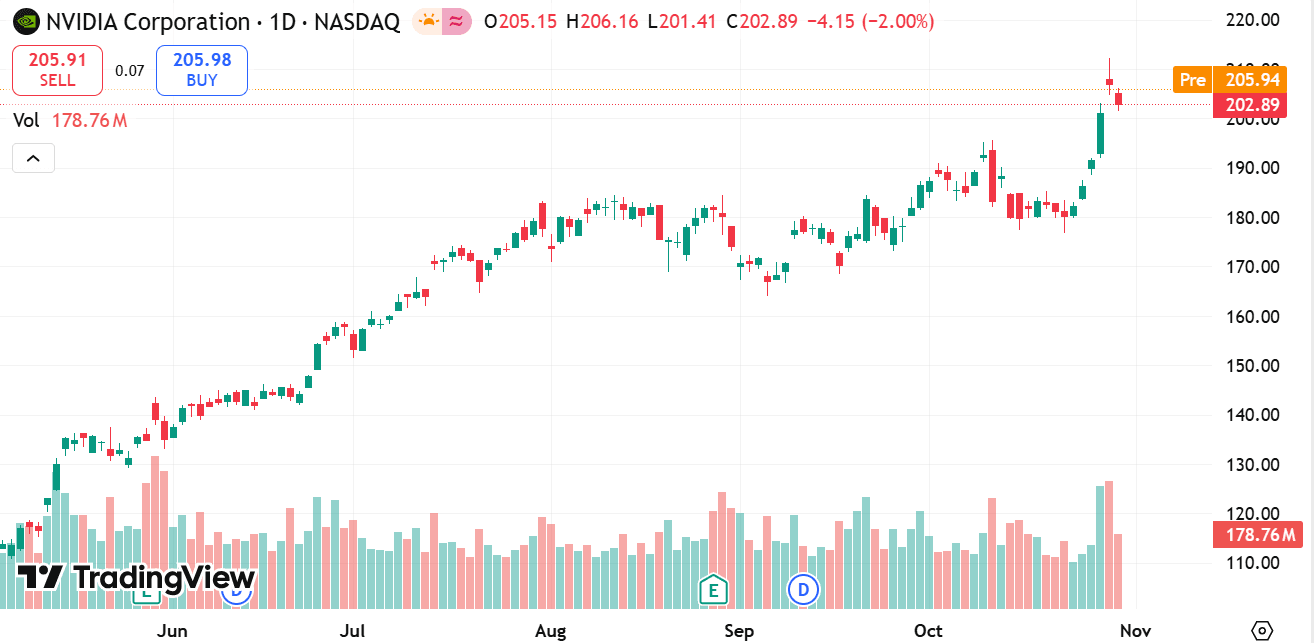
source: tradingview
While learning established methods is helpful, developing a personalized approach tailored to one’s preferences, schedule, and temperament can lead to better consistency.
Define Your Time Frame
Day trading time frames can vary from a few minutes to several hours within the trading session. Decide what suits your lifestyle and ability to focus. Some prefer ultra-short trades, while others may hold positions for a few hours.
Select Suitable Markets
Not all markets behave the same way. Some offer more volatility and liquidity, which are generally favorable for day trading. Select markets where you can monitor price action closely and where trading costs are manageable.
Develop a Routine
Consistent routines help prepare mentally and physically for the demands of day trading. This includes reviewing economic calendars for scheduled events, scanning markets for setups, and performing post-session reviews.
Test and Refine
Before risking real capital, test your method through simulation or small position sizes. Keep a trading journal to record trades, reasoning, and outcomes. This feedback loop is invaluable for refining strategies and improving discipline.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Day trading is challenging and mistakes can be costly. Awareness of common pitfalls helps reduce unnecessary setbacks.
There is no one-size-fits-all best method for day trading. The most effective approach combines well-defined entry and exit rules, strict risk management, emotional discipline, and adaptability. Popular methods like momentum, scalping, reversal, and breakout trading provide frameworks that can be tailored to individual preferences.
Building a personalized day trading method involves selecting time frames, markets, and routines that align with your lifestyle and learning style. Continuous practice, review, and refinement are key to improving over time.
Day trading demands focus, patience, and resilience, but with a structured method and realistic expectations, it can become a manageable and engaging way to participate in financial markets.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.